What is markdown?
Markdown is a lightweight markup language for creating formatted text using a plain-text editor [1]. It is popular format for documentation and other text-based content.
As the amount of information grows, the files can become long and difficult to manage. The solution to this problem is to break down the markdown file into smaller, more manageable topics and then compile them into a single file.
Step-by-step guide
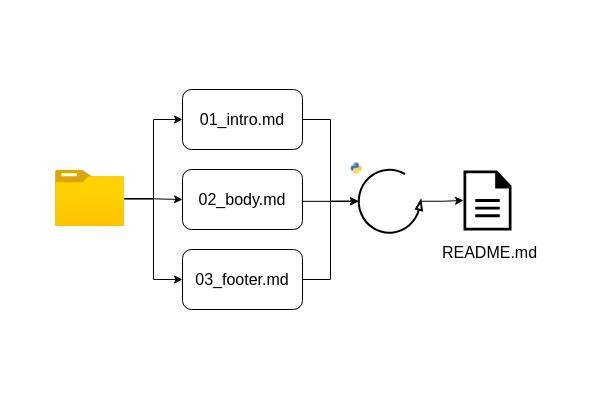
Here's a step-by-step guide to organizing your markdown files and compiling them into a single README.md file using the following Python script.
First of all, organize your markdown files by numbering them in sequence order, using a naming convention like "00", "01", "02", and so on, in ascending order.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
_LOC = '../docs'
OUTPUT_MD = '../README.md'
def make_readme():
"""
Compiles markdown files into single README.md.
"""
with open(OUTPUT_MD, 'w') as output_file:
for file_name in sorted(os.listdir(_LOC)):
with open(os.path.join(_LOC, file_name)) as input_file:
output_file.write(input_file.read())
make_readme()This script reads a set of markdown files from a specified location, _LOC, and compiles them into a single README.md file located at OUTPUT_MD. The file names are sorted to ensure that the content appears in the desired order in the output file. By numbering your markdown files in ascending order, you can ensure that the content appears in the desired order in the final README.md file.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the use of Python for managing markdown files provides a quick and efficient solution for managing long and tedious markdown content. Whether you are working on a project with many topics or simply want to simplify your documentation process, this script is a useful tool to have in your toolbox.
Articles recommended by the author:
References
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markdown
[2] Source code